Coccidiosis
ARTICLE SUMMARY
Coccidiosis is a parasitic disease of poultry caused by protozoans of the genus Eimeria, affecting mainly chickens and turkeys. It impacts the intestinal tract, leading to poor feed conversion, slowed growth, higher mortality, and substantial economic losses worldwide.
While anticoccidial drugs (ionophores, chemicals) have long been standard for prevention, vaccination is increasingly adopted as a more sustainable and effective control method.
Key takeaways :
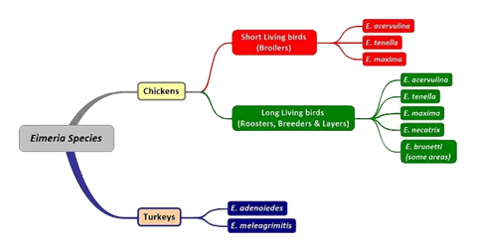
- Multiple Eimeria species (nine in chickens) can cause coccidiosis; depending on species, lesions may appear in the caeca or small intestine.
- The parasite’s lifecycle involves oocysts shed in feces, sporulation in the environment, ingestion by birds, then successive intracellular cycles ; a lifecycle that can repeat every 5–8 days and results in exponential parasite amplification.
- Vaccination (e.g. with live-oral vaccines) offers effective immunity by exposing birds to low-level infection, prompting cellular immune responses; this strategy reduces reliance on anticoccidial drugs and helps manage resistance issues.
What Causes Coccidiosis on Chickens ?
Nine species of Eimeria are capable of infecting chickens
Depending on the localization of lesions in the intestines, coccidiosis are divided into caecal, induced by E. tenella, and small intestinal, induced by E. acervulina, E. brunetti, E. maxima, E. mitis, E. mivati, E. necatrix, and E. praecox. All are intracellular parasites belonging to the Eimeria genus of the Eimeridae family. The exogenous development of Eimeria in poultry consists of forming in their oocysts, 4 sporocysts with 2 sporozoites each. This process, called sporulation, happens only under suitable external conditions, adequate warmth (the optimal temperature is 29°C), moisture and oxygen.
The sporulation process usually occurs within 24–48 hours after excretion. At temperatures below 8°C, most of the unsporulated oocysts perish, but in those which survive, sporulation could go on for more than 8 weeks (Obreshkov et al., 1978). Eimeria in poultry is very host specific.
Symptom of Coccidiosis in Chicken
Common signs in infected flocks include reduced feed consumption, rapid weight loss, droopiness, ruffled feathers, and severe diarrhea. Wet droppings with mucus are common. Clinical infections are seldom seen in poults >8 wk old. Morbidity and mortality may be high.
Diarrhea, which may become bloody in severe cases, is the primary symptom. Most animals infected with coccidia are asymptomatic, but young or immunocompromised animals may suffer severe symptoms and death.

Disease Lifecycle
Depending on the Eimeria species, the coccidian lifecycle takes approximately five to eight days to complete.
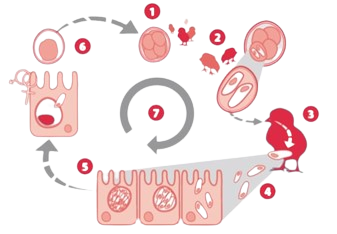
Stage 1 : Unsporulated oocysts are shed in the feces in the litter. Oocysts sporulate (become infective) in the presence of adequate moisture, oxygen and temperature. Oocysts are extremely environmentally resistant and can survive up to one year in dry, cool environments.
Stage 2 : Sporulated oocysts, containing four sporocysts that each contain two infective sporozoites, are ingested by the birds from ground and litter pecking.
Stage 3 : Sporocysts and then sporozoites are released in the gut from the sporulated oocyst by excystation, a process facilitated by the physical grinding effect and the presence of digestive enzymes and bile salts.
Stage 4 : The sporozoites penetrate the gut cells to initiate development of asexual intracellular schizonts. Schizonts produce large numbers of a second invasive stage, called merozoites that penetrate other gut cells to produce a further generation of schizonts.
Development of immunity
In general, the development of immunity is a complex process. With Eimeria, the process is further complicated by the parasite's multifaceted lifecycle, with each stage presenting a different set of antigens to the immune system for recognition and response.
Although both cellular and humoral immune responses are stimulated during coccidiosis, they differ in the extent to which they respond to the infection. Since most of the Eimeria lifecycle occurs intracellularly, the most effective immune response is of a cellular nature, not a humoral one.

The development of immunity is also influenced by the level of parasite infection. In a heavy infection, the immune system reacts with a short-term humoral immune response. In a low level infection, such is produced by vaccination, the immune system reacts with a cellular immune response that offers a more complete, longer term immunity against the parasite.
The relative short duration of this type of immunity requires a constant exposure to a low level circulating Eimeria to sustain a protective level of immunity.
Download your Coccidiosis Manual now
![Coccidiosis extrait[2259]-1](https://4368135.fs1.hubspotusercontent-na1.net/hubfs/4368135/Coccidiosis%20extrait%5B2259%5D-1.png)





